FAQ
1.Hydraulic Oil: Check if the hydraulic oil is between min. and max. line of oil gauge? If the toggle auto filler oil at proper level?
2. Cooling water: Check if the cooling water pipe is free of leakage and if water level sufficient to have normal cooling effect.
3. Start heating element and check: Ensure the electric heater of dryer, barrel and mold are at normal condition, especially the temperature must reach the set temperature before working injection, retreat and screwing motions.
4. Check the safety door and safety rod: Ensure the opening and closing of safety doors are normal, and the contact between safety door and each limit switch and the pressure relief valve are normal. Ensure the safety rod is proper position and firmly locked. Ensure the red press buttons on the operation box are working normally, so as to ensure the safety of operator.
5. Lubricating device check: Check if the grease oil level is sufficient and the filler time setting is proper and the filing device piping are unimpeded?
6. Moving mechanism check: All moving mechanism shall have proper lubrication, and the debris and dust on the moving parts shall be cleaned and maintain the friction surface clean and smooth. No tool shall be placed on moving parts, so to avoid breaking while machine is in operation.
7. Low pressure mold closing device check: Correctly adjust low pressure mold closing device to ensure the safety of mold.
8. Check other conditions: Ensure all settings, such as temperature, pressure, speed, timing and distance are correct.
9. Load free check: Work full-auto operation at lower pressure and let it run load-free for 10 to
30 min. and commence normal operation after a steady working condition is reached.
10. Noise check: Record the sounds at normal operation and the sound of hydraulic pump, it will allow operator to detect abnormality like blocking of filter, air-intake, internal wear. The buzz sound of solenoid is related to the debris in the internal axis. The buzz sound of relay and magnetic contact indicate dirt and dust existence at the contact. Check the cause of the noise will be helpful in preventing damage.
1. Shut the gate of material hopper and reduce or close the heating device of hopper (depends on
the length of time of the stop.
2. Shoot out all the resin in the material pipe, particularly acid and corrosive materials must be totally cleaned up.
3. Wipe mold to clean and apply anti-rust treatment. (depend on the length of time stopping operation)
4. When machine stopped, if the mold is not removed, do not extend toggle straight.
5. Close cooling water and switch off power.
6.Clean machine.
Weekly regular check
1. Heater check—Check for any broken wire or ill contact. (For CE model, check the reading of amp meter).
2. Leakage check—Check the fittings of cylinder, oil pipe and solenoid for leakage.
3. Screw and nut check—Check the bolts, screws and nuts of the whole machine for any loss or loose.
4. Nozzle heater band check—remove any and all material attached to the lead wire and nozzle heater band.
5. Remove deposited waste oil on the machine.
6. Filtering mesh cleaning- within the first month, clean it every week, thereafter on monthly basis. Clean the whole machine.
Monthly regular check
1. Perform stricter check as per the weekly items and in determined manner.
2. Grounded wire check: grounded wire shall be checked strictly to ensure the user would not suffer electric shock.
3. Electric wire check: Electrical parts are likely to loose off due to vibration, burnt due to increase in current. So the terminal screws must be fasten firmly, and the dust, foreign matters and oxidation on the contact must be removed.
4. Movable mold platen and hydraulic motor seat skate check: check if the skate worn out, screw loose and moving parts are lubricated.
5. Cleaning and check of cooler: if underground, industrial water or salt water is used, remove the cooler to clean on monthly basis to improve and extend the efficiency and service life of cooler. If ordinary tap water is used, it may be cleaned in six-month interval (Basically, soft water is preferred, and add soften agent and scaling agent.)
Six-Month regular check
1. Repeat the monthly items in stricter and firmer attitude.
2. Hydraulic oil regular check: ask the oil supplier to make regular check of hydraulic oil to ensure the quality of hydraulic oil.
3. Check for any abnormal wearing of the moving part of machine.
Annual regular check
1. Repeat the half-year items in stricter and firmer attitude.
2. Electric motor check: Clean the intake port of cooling portion of electric motor with steel brush or air blower, because any dirt or dust exists, it will cause the motor to heat up and result to other heat damage directly.
3. Ventilation system check: Ventilation window installed on closed machine is for ventilation, so the oil stain and dirt attached shall be cleaned to prevent damage due to heating or cause oil temperature to rise.
4. Insulation check: The insulation of wire cover is downgrading gradually, so it is necessary to perform insulation measure to avoid accidental electric leakage and identifying earlier will permit prevention.
Generally, plastics can be split into 2 categories, thermoplastic and thermosetting.
Under ambienttemperature, thermoplastic is in granular type and when heated to certain temperature, it will becomemolten and when cool down, it will be solidified to a form. If heat again, it will become molten again fornext plastering.
Hence, thermoplastics can be molded through heating to molten and repeatedsolidification. So there is so called secondary material. On the other hand, thermosetting plastic issolidified when heated to a certain temperature, and even heat up again, the status will not change again.
So, thermosetting plastics cannot be heated to repeat the molding. Therefore, thermosetting wastematerial is normally unable to recycle.
The categorization is shown as the following figure.
Abbreviation :UP(Unsaturated Polyester)、EP(Epoxy Resin)、PF(Phenolic Resin)、MF(Melamine Resin)、UF(Urea Resin)、SI(Silicone Resin)、PI(Polyimide)、PU(Polyurethane)、PABM(Polyamidebismaleimide)、BT(Bismaleimide-triazine)、 DAP(Polyarylphthalate)
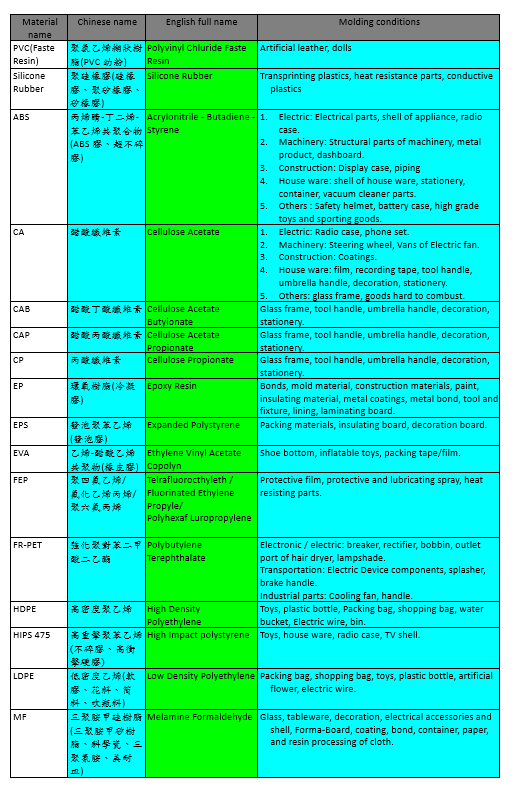
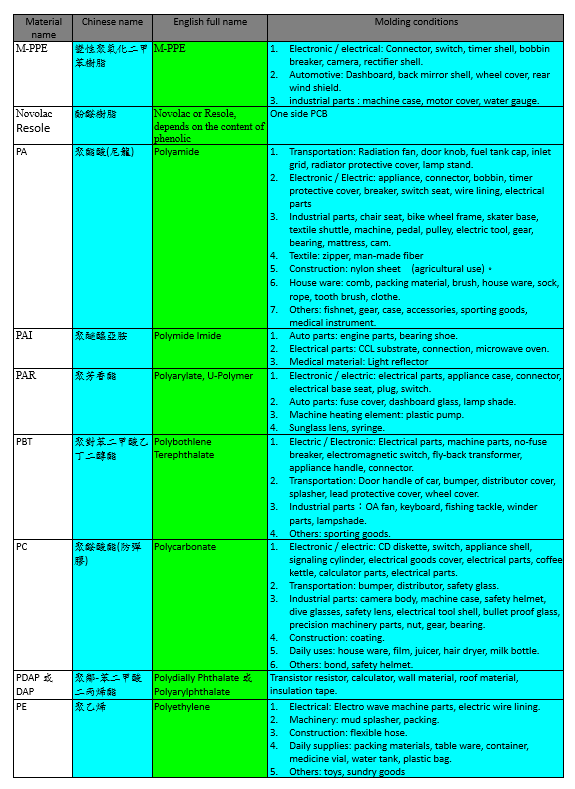
The following are the characteristics of frequently used plastic materials, list down for reference.
Engineering plastic is industrial plastic made to be industrial parts or shell. Their strength, impact resistance, heat resistance, hardness and aging resistance are all good. In Japan, the industries define them as “high performance plastics used as mechanical parts with heat resistance at 100℃ or higher and mainly for industrial use”.
Their property include:
- Thermal Property: High glass transfer temperature (Tg) and melting point (Tm), high temp.Deformation, high long-term use temperature (UL-746B), large use temperature range, low heat expansion coefficient.
- Mechanical property: high strength, high mechanical mode, low creep, abrasion resisting, fatigue resisting.
- Others: Good chemical resistance, good electric resistance, combustion resistance, weather resistance and dimensional stability.
Those being used as universal plastics include Polycarbonate, PC, Nylon, Polyamide, PA, Polyacetal, Polyoxy Methylene, POM, M-Poly Phenylene Oxide, M-PPE, PETP, PBTP, Polyphenylene Sulfide, PPS, and in thermosetting plastics there are saturated polyester, phenolic plastic and epoxy. They have stretch strength all exceeding 50Mpa and tensile strength over 500kg/cm2, impact resistance exceeding 50J/m, bending elasticity at 24000kg/cm2, load flexible temperature over 100℃. Good hardness and aging property. When PP has the hardness and cold resistance improved, it can be categorized into engineering plastics. Also included are fluorous plastics, which are low strength, good heat resistance and medicine resistance, silicone molten compound of good heat resistance, polyetherimide, polyimid, Polybismaleimide、Polysufone(PSF)、PES、PP Plastic, M-Millitic Amine Plastic, BT Resin、PEEK, PEI, crystalline plastic. Due to difference in chemical structure, medicine resistance, friction characteristics and electric characteristic are different. Due also to the molding property, part of them are suitable for all kinds of molding, and some of them fit only to certain types, which restricted their applicability. Thermosetting engineering plastics are with poor impact resistance, so the normally are added with fiberglass. Other than PC, which has high impact resistance, they normally have low elongation, hard and brittle, but if they are added with 20 – 30 % fiberglass, they can be improved.
Plastic is a aggregate of slim, linear polymer compound. The regularity of molecular array is called crystalline, the degree of crystallization, which can be measured with X ray. Organic compound has more complicate construction, and the bonds are various (linear, curl, folding, spiral, etc) and this leads to great change in construction due to molding conditions. Plastics with high crystallization are Crystalline Plastics, and the interaction is high between molecular and become tough plastic. To be crystallized and correct regular array, the volume becomes smaller and the shrinkage and heat expansion rates become larger. Hence, the higher the crystalline is, the poorer the transparency and the higher the strength.
Crystalline Plastics has apparent melting point (Tm), at solid state, it is arrayed regularly, the strength is higher and the tensile is better. When melted, there is higher specific volume change and easy to shrink after solidification. The inner stress is less easy to release. The molded product is non-transparent. The heat dissipation during molding is slow. Production with cold mold has large shrinkage rate, but smaller in hot mold production. In contrast, there is Non-Crystalline Plastics. It does not have apparent melting point, and the molecular is not regularly arranged in its solid state. When melted, there is small change in specific volume, and not likely to shrink when solidified. The product has good transparency. The higher the material temperature, the yellowish the gloss is. Heat dissipation is fast during molding. The following is comparison of property of the two different kinds.
The full name of MI is Melt Flow Index, or Melt Index, a value indicating the fluidity of plastic at working. It is established by ASTM adopting the method normally employed by Du Pont is testing characteristics of plastics. The testing method is the weight in gram of plastic material flowing through a round tube of 2.1mm within 10 minutes under certain temperature and pressure (they are different for different type of plastic materials). The higher the value the better the working fluidity of the specific plastic material, or it is poorer. The most frequent test standard is ASTM D 1238. The measuring instrument of this standard is Melt Indexer, with construction of one trough for plastic material; a tube of 2.095mm dia. and 8mm long is fitted to the end of the trough. When heated to a certain temperature, a piston at the top apply certain weight and press down to measure the weight of the material being squeezed out in 10 minutes, which is the MI. Sometimes, it is indicated as 25g / 10min, clearly indicate its MI is 25, and is 25g being squeezed out in 10 min. The MI values of frequent used plastics are ranged between 1 and 25. The higher MI the lower the viscosity and mole weight, and the smaller MI is, the plastic has higher viscosity and large mole weight.
Glass transition temperature, Tg, is a kind of Transition temperature. AT Tg, polymer will demonstrate rubber state at higher temperature to hard and brittle glass-like state at lower temperature.
Crystalline plastics have apparent Tg and latent heat. A polymer in rubber or glass state is depends on Tg and the temperature in use, so Tg is an important indicator in the use of polymer.
The following are Tg of some of plastic materials.
Heat deflection temperature, HDT, means , under pressure, the highest temperature the plastics maintain profile unchanged. Generally, this is indicated by Short Term Heat Resistance of plastics. When safety factor is taken into consideration, the highest temperature at use shall be 10℃ less than HDT. The most frequent used measure is ASTM D648 (apply temperature rise of 2℃/min at the center of a standard of 127×13×3mm, under 455kPa 1820kPa charge, till the deformation rate is 0.25mm). For non-crystalline plastics, HDT is 10~20℃ Tg; to crystalline plastics, HDT is close to Tm. Normally, when fiber reinforcement is added, the HDT will rise, because the fiber can greatly increase the mechanical strength of plastics, so the HDT will rise drastically during temperature rise flexibility test.
Shrinkage rate means the deviation in dimensions of the molded , cooled and solidified products from the dimension of original molds measured in percentage, this can be measured per ASTM D955.
The shrinkage rate shall be considered firstly at the design of mold, so to avoid the product discrepancy due to dimensional discrepancy.
The scope of application of certain frequently used plastics:
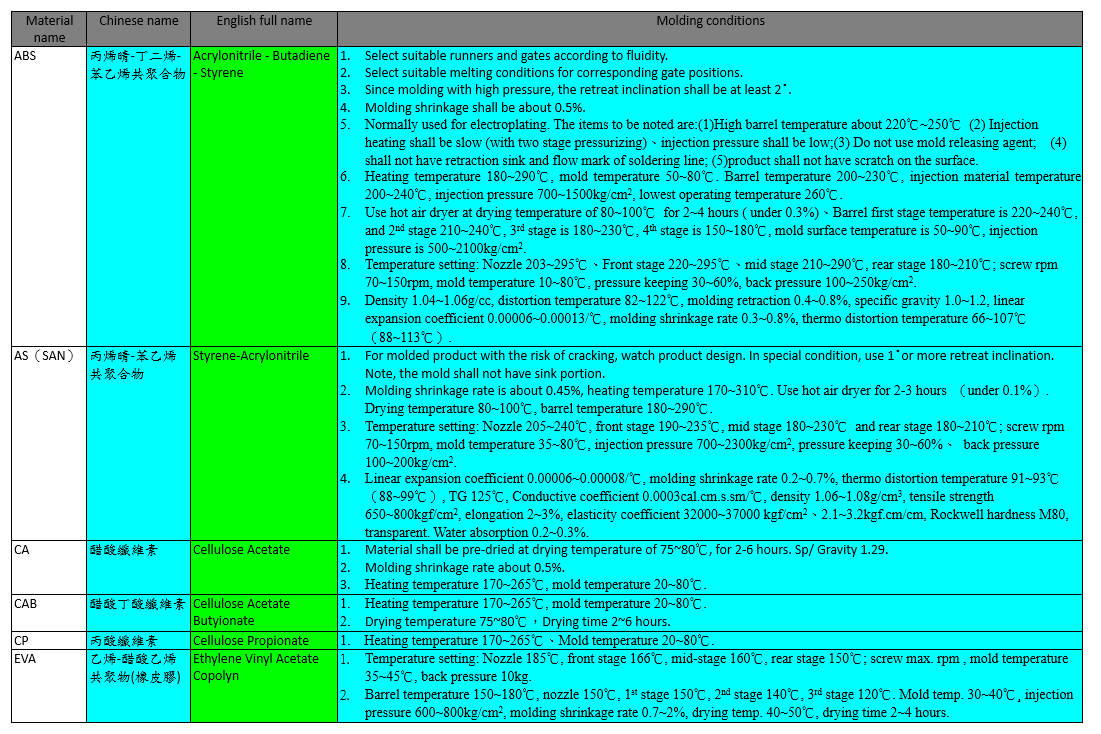
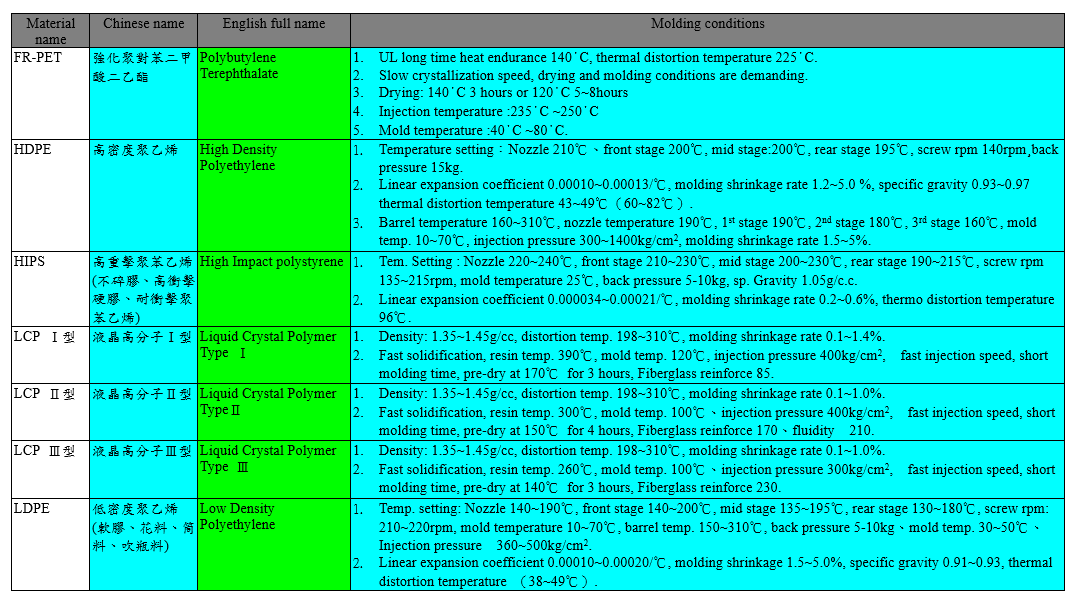
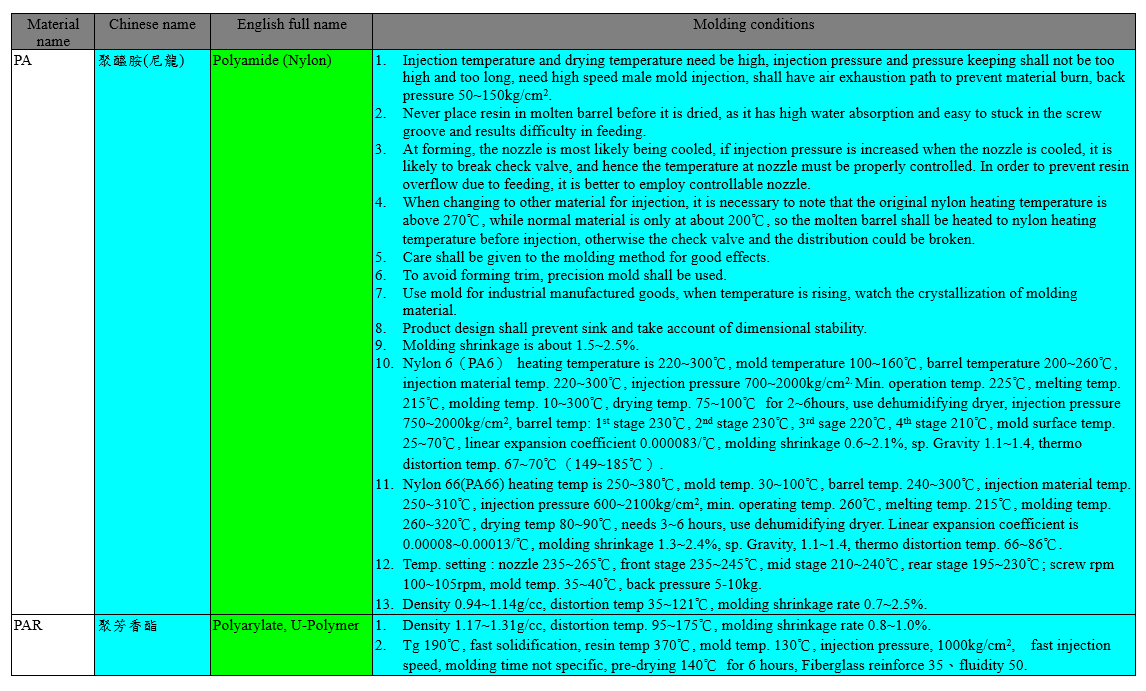
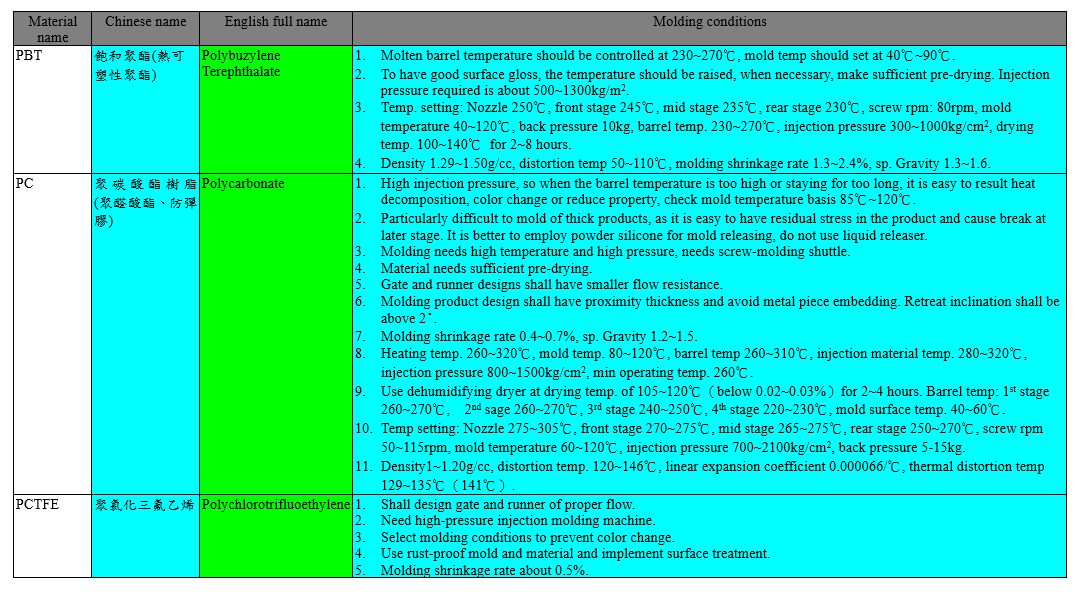
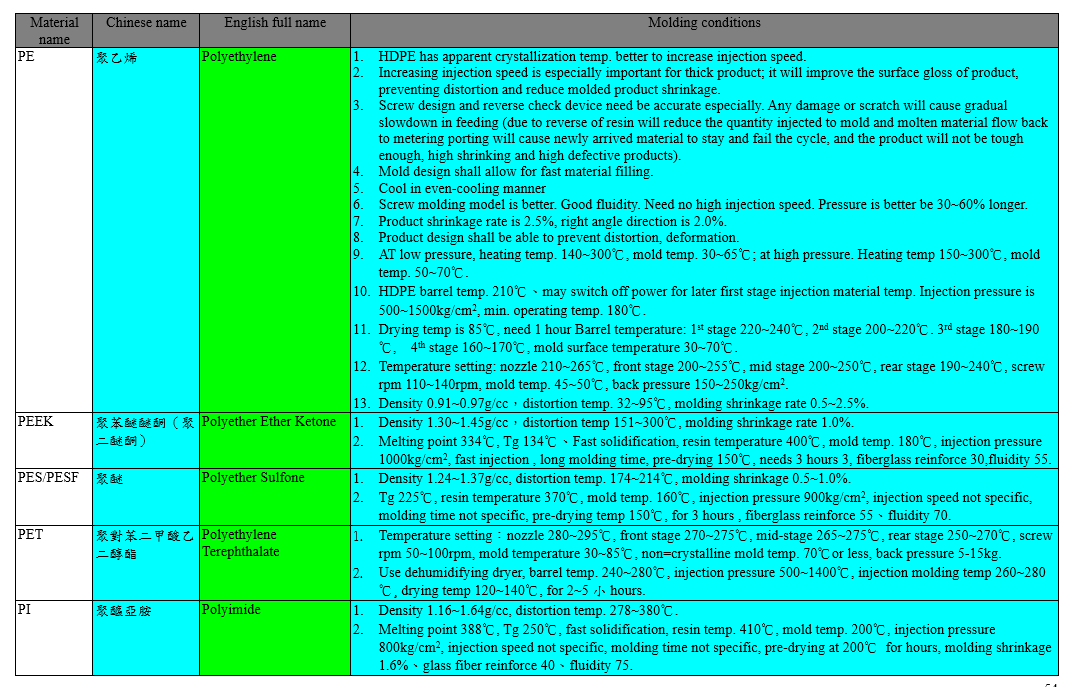
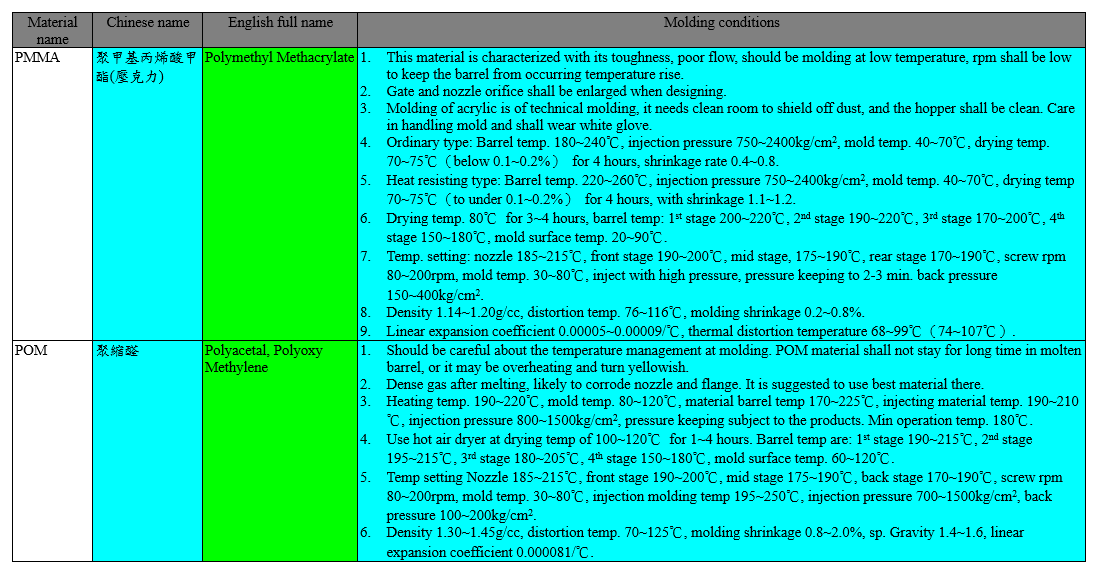
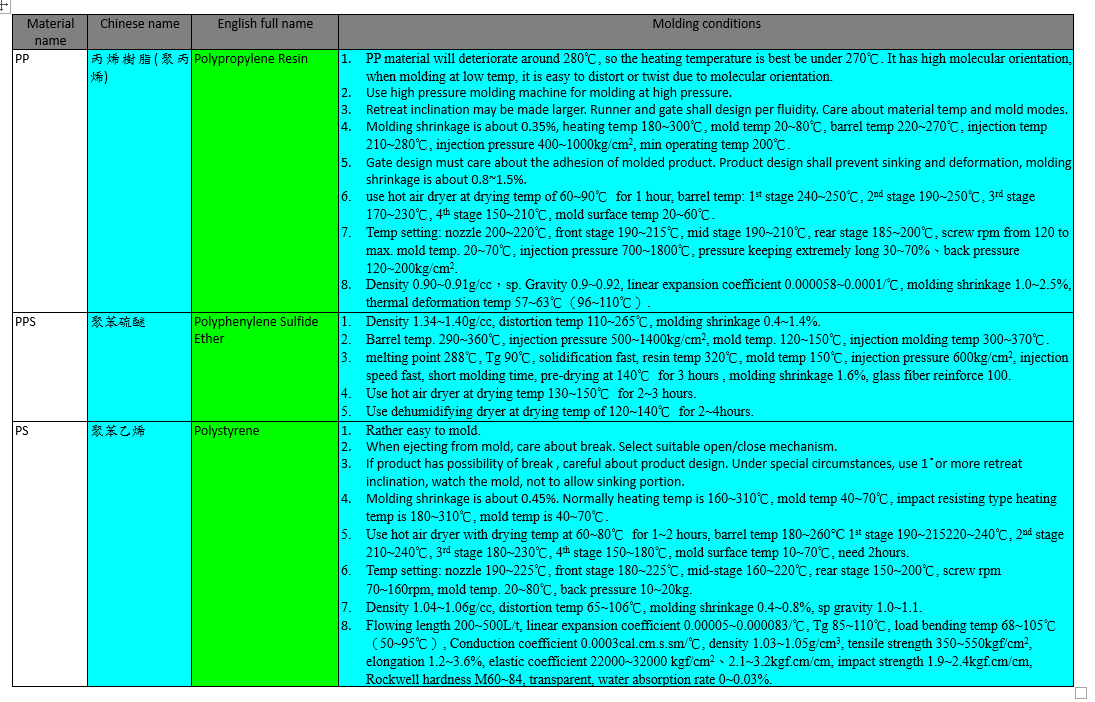
The molding conditions of some plastic materials are listed in the following tables:
Injection mold can be split into hot runner mold and cold runner mold. The former is also called as “ No Runner Mold” which insert heater into sprue or runner to keep the molten resin at this portion to coagulate but flowing. After each injection, the material in runner will remain there and taken out on the product,which means during the resin is the mold cavity, the resin in the runner remain molten, and when open mold, only the product is taken out. The later type of mold, the resin in the runner cools down together with the resin in the mold cavity, and takes out together. It is further split into Cold Runner 2-platen mold and Cold runner 3-platen mold.
In cold runner 2-platen mold, the product and the gate are taken out together, except submersible gate, the product and runner is connected. In cold runner 3-platen mold, after opening the mold, the product and the gate are taken out together also, but mostly with point gate. The difference between them is that the runner is set to the other plane of mold splitting surface in case of cold runner 3-platen mold, which means that except Core and Cavity, there is another a runner releasing plate. The mold is basically consisted of these 3 mold platens, and the fixed mold plate and runner releasing plate are sliding along the long guide key on the installation plate of the fixed portion